March 23rd, 2025
AI Chatbot vs. AI Agent: What’s the Difference?
By Connor Martin · 6 min read

Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a major force in technology. Yet, the industry is still only in its infancy. The “Age of AI” only really kicked off in late 2022, with the release of ChatGPT. However, many people are still learning how it all works, including technology such as AI chatbots and AI agents.
There is still a lot of confusion about these terms. Since they are often used interchangeably, many people mistakenly believe they refer to the same thing. However, they do not. AI agents and chatbots are two distinct, separate entities. This AI chatbot vs. AI agent guide will examine the key differences between them and the unique roles of each one.
Key Takeaways
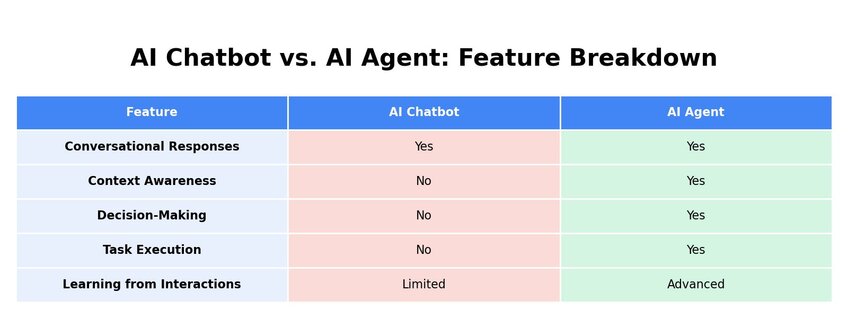
• AI chatbots vs. AI agents: AI chatbots are designed for basic conversational interactions, while AI agents are more advanced and capable of autonomous decision-making, learning, and executing complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
• Functionality and adaptability: AI agents have greater contextual awareness, can analyze data, and improve over time, making them suitable for a wide range of industries beyond customer support, such as finance, healthcare, and logistics.
• Choosing the right AI solution: AI chatbots are cost-effective for simple tasks like customer inquiries, while AI agents provide superior scalability, automation, and integration for businesses needing advanced AI-driven solutions.
What Is an AI Chatbot?
An AI chatbot is a conversational tool able to carry out basic back-and-forth dialogue with users. Chatbots have been around for many years. The older ones simply provided a fixed set of responses based on user input. Modern AI chatbots are more advanced, using natural language processing technology to interpret the user’s demand and generate a specifically tailored reply.
Well-known and widely-used examples of AI chatbots are Google Assistant and Siri. Many brands also employ their own AI chatbots to respond to customer inquiries and manage basic customer interactions, like helping people find a product on a website, place an order, or troubleshoot a tech problem. They are mostly useful for carrying out repetitive tasks, freeing up human agents for more important tasks.
Types of AI Chatbots
AI chatbots can vary in their intelligence and utility, as well as their ways of working. Some are quite basic, with only limited learning capabilities, while others are capable of performing complex tasks and managing both text and voice interactions. Varieties include:
• Menu-Based: Similar to old-fashioned chatbots of the past, menu-based models simply present the user with a menu of options. The user can then navigate the scripted, preset menu to access the function or response they need.
• Rule-Based: The next step up from menu-based models, rule-based bots have a set of if/then rules to follow. This allows them to deliver more customized and precise responses to different user inputs.
• Generative: Many modern AI chatbots are generative models. They use natural language understanding to effectively work out what a user wants and generate a customized response rather than plucking a preset response from a limited set of options.
We can also divide AI chatbots according to their roles. There are customer service or support bots, for example, often employed by retail firms and other businesses to respond to customer queries. There are also IT support chatbots that help users troubleshoot tech issues, or booking and reservation bots – mainly used in hospitality – to help guests make bookings without having to call or speak with a human.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an intelligent digital assistant. Like the best AI chatbots, AI agents use natural language and machine learning technology to process and respond to user input. They can also be referred to by various other names, like intelligent assistant or AI assistant. They can handle complex tasks to a much higher standard than a simple chatbot and are more sophisticated in terms of:
• Context awareness, which helps them understand the nature of a user’s inquiry
• Data analysis, as they can review vast data sets and real-time info to deliver accurate replies
• Autonomy, allowing them to not only generate replies but also solve problems and make decisions
• Learning, as these agents can review past interactions and user behavior to improve future conversations
The more advanced nature of an AI agent vs. a chatbot allows autonomous AI agents to conduct a wider array of complex tasks and business processes, with only minimal human intervention. They can be used in industries as diverse as finance, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and marketing and can help not only customers but workers and team leaders with a multitude of tasks.
Key AI Agent Technologies
To better understand what AI agents offer, here is a look at some of their core technologies and capabilities:
• Natural Language Processing: The ability to process and comprehend human language in text or voice format
• Contextual Understanding: Using contextual cues to comprehend a user’s needs, intentions, and even their mood, reinforcing correct responses
• Decision-Making: The ability to analyze data, make predictions, and weigh up possible outcomes to make informed decisions
• Autonomous Task Execution: Empowers AI agents to not only submit responses and generate content but also create and implement entire tasks on their own
• Dynamic Learning: Enables AI agents to employ deep learning from their interactions to deliver better performance in the future• Multi-Modal Capacities: Allows modern AI agents to interact with and generate content in different formats, like text, image, video, code, and voice. This multi-modality powers the AI video agent, enabling it to produce high-quality videos with minimal human input.
AI Chatbot vs. AI Agent: 5 Differences
Next, let’s look at five of the key differences separating chatbots and AI agents. These differences will reveal the fundamental divide between the two groups in terms of intelligence, utility, and versatility.
Task Complexity and Capability
AI agents are capable of far more complex tasks than chatbots and boast superior levels of intelligence and utility on the whole. They can handle an increasingly vast array of processes, which can include everything from conducting safety checks in warehouse environments to plotting out the most appropriate marketing channels a brand should focus on to increase its exposure.
As mentioned earlier, their applications can be seen in many different industries, from finance to medicine and beyond. They can be programmed and given a range of data sets to learn from, enabling them to carry out a large range of processes. By contrast, AI chatbots are much more grounded in fields like customer support and simple “query and answer” interactions with users.
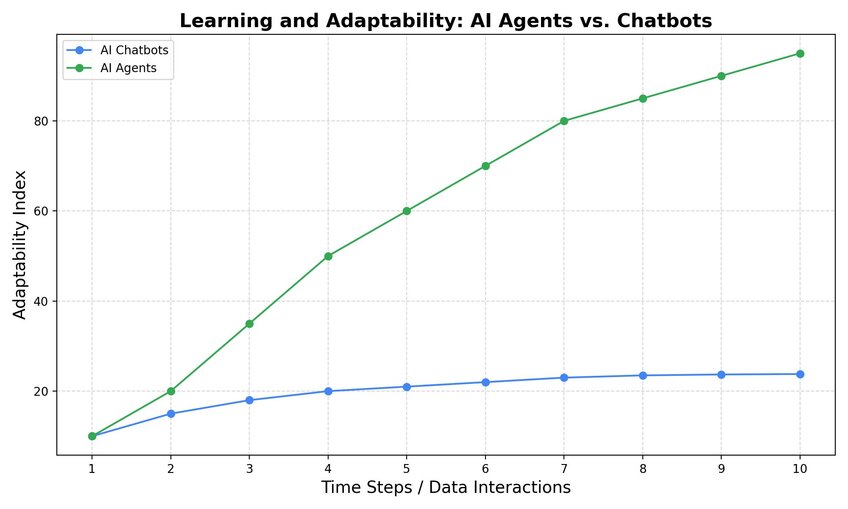
Learning and Adaptability
Most chatbots are very limited in terms of their learning potential. They are often given a small, fixed range of functions to employ in the course of their routine operations. An IT support chatbot, for example, will simply be able to provide users with a range of go-to troubleshooting steps or solutions or redirect them to a human agent, if needed.
AI agents, meanwhile, are much more sophisticated, overall, in terms of their learning. They are continuously improving, gaining valuable data through their interactions with customers. They grow more advanced with each usage and have the potential to adapt to a much broader range of situations and user inputs.
Context Awareness and Personalization
Contextual awareness is one of the core features that separates AI agents from chatbots. In a nutshell, this term refers to an AI tool’s ability to understand the context around a user demand or to effectively see beyond the user’s words, in order to know more about what they are asking and why they need it. This improves their ability to deliver tailored, suitable responses in every situation.
AI chatbots rarely, if ever, have much contextual awareness. They are programmed to interpret a user’s demand and deliver a fixed response. However, when given the same sort of input, intelligent and aware agents are able to understand the user’s needs, emotional state, and preferences to generate an adaptive response. This leads to more satisfaction and utility.
Integration and Automation
While both chatbots and AI agents deliver automated customer responses, a downside with many bots is that they will frequently need human intervention. This is due to their limited range of functions and responses. There are many situations in which a chatbot will not be able to deliver exactly what a user needs, and will instead redirect them to a human agent.
In contrast, because of their learning potential and contextual understanding, AI agents can often resolve user inputs and automate complex tasks more efficiently, with far less human intervention needed for support. They also boast superior and far-reaching integration and can work alongside various other tools in many industry settings.
Flexibility and Range of Use Cases
When comparing AI chatbot vs. AI agent use cases, it is easy to see how much more flexible, advanced, and helpful AI agents are. There are financial AI agents that can assess market data to predict upcoming trends, agents in healthcare that can deliver tailored treatment recommendations in alignment with patient data and history, and asset management agents used to track and manage inventories efficiently.
There are many more examples of AI agents that have been effectively taught to aid with almost any digital business task. Chatbots simply do not have the same range. They are almost exclusively customer-facing tools used for support and general assistance, like the aforementioned examples of IT troubleshooting or making a restaurant reservation.
How to Choose Between an AI Chatbot and an AI Agent
Choosing between an AI chatbot vs. AI agent is simply a matter of assessing your needs and selecting the most fitting solution. In the vast majority of cases, an AI agent will be the right call, as agents are superior in most areas like intelligence, adaptability, and flexibility. However, they are not necessarily the one and only solution in every situation, and chatbots still have a place in the world.
Consider these factors to inform your decision:
• Intended Use: This is the main factor, as many use cases will only work if you employ an AI agent – a chatbot will often lack the functionality and versatility needed for logistics processes or financial forecasting, for example. For simpler use cases, like user support and repetitive customer interactions, a chatbot may be enough.
• Budget: One aspect that may scupper your ability to make full use of an AI agent is your budget. Agents are more costly to develop, implement, and maintain than chatbots. So, those with limited resources are better off sticking with chatbots in most cases, as you will need a larger budget to enjoy the advantages of an agent.
• Scalability: Do not only think of the present but also look to the future. Imagine how your needs for your AI tool might change or evolve in the months ahead. If you expect that you will need your AI aid to take on additional tasks or adapt to changing conditions, an agent will be the right option, because of its adaptable, scalable nature.
• Security: From a security standpoint, there can be challenges working with AI agents. Because of their broader scope and use cases, it can require more effort and care to ensure that any sensitive data they handle is kept safe and in accordance with compliance regulations. Chatbots, as simpler entities, are somewhat easier to manage in this respect.
Stay Ahead of the AI Curve With Julius AI. Try It Out Today for Free
Overall, AI agents are more efficient, intelligent, and effective than mere chatbots, and Julius AI is a testament to that. Julius AI is a leading AI data analyst, capable of interpreting vast sets of data far faster than any human. It can carry out countless forms of statistical analysis, create data visualizations, and much more.
Test it today to see the benefits firsthand.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a chatbot and an AI agent?
An AI chatbot is a conversational tool designed to handle basic interactions, typically responding to user queries with scripted or AI-generated replies. An AI agent, on the other hand, is a more advanced system capable of learning, making decisions, and executing complex tasks autonomously, often integrating with broader workflows and data-driven processes.
What is the difference between AI and AI agents?
AI (artificial intelligence) is a broad term that encompasses all technologies enabling machines to perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as data analysis, language understanding, and decision-making. AI agents are a specific application of AI, designed to act autonomously, process context, and execute multi-step tasks with minimal human intervention.
What is an example of an AI agent?
A well-known example of an AI agent is IBM Watson, which can analyze vast datasets, assist in medical diagnoses, and provide industry-specific insights. AI agents are also used in finance for automated trading, in supply chain management for logistics optimization, and in customer service for personalized recommendations.
What is an example of an AI chatbot?
A common example of an AI chatbot is ChatGPT, which engages in natural language conversations and generates responses based on user input. Other well-known chatbots include virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, which help users with simple queries, reminders, and daily tasks.
What does an AI agent do?
An AI agent processes data, understands context, and autonomously executes tasks across various domains, from automating business workflows to providing real-time analytics. It can make decisions, adapt based on past interactions, and integrate with other systems to improve efficiency and accuracy in operations.
