April 4th, 2024
Conducting and Interpreting Factor Analysis
By Josephine Santos · 11 min read

Overview
Factor Analysis, a powerful statistical method, is akin to cluster analysis but with a twist. While cluster analysis groups similar cases, factor analysis groups similar variables into dimensions, unveiling latent variables or constructs. This technique is pivotal in simplifying complex datasets, especially when the goal is to reduce a plethora of individual items into fewer dimensions.
The Essence of Factor Analysis
Factor Analysis serves multiple purposes:
1. Data Simplification: It's a tool to reduce the number of variables, especially beneficial in regression models.
2. Rotation Methods: Post extraction, factors are usually rotated. Various rotation methods exist, with some ensuring factors remain orthogonal, thus eliminating multicollinearity issues in regression.
3.Scale Verification: Factor analysis aids in verifying scale construction. Confirmatory factor analysis, a subset, is used in structural equation modeling.
4. Index Construction: While the common approach to construct an index is summing up all items, factor analysis can justify dropping certain questions to make questionnaires concise.
Using SPSS for Factor Analysis
To understand the underlying dimensions of standardized and aptitude test scores, SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is a go-to statistical software. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1.) Locate Factor Analysis: Navigate to Analyze > Dimension Reduction > Factor.
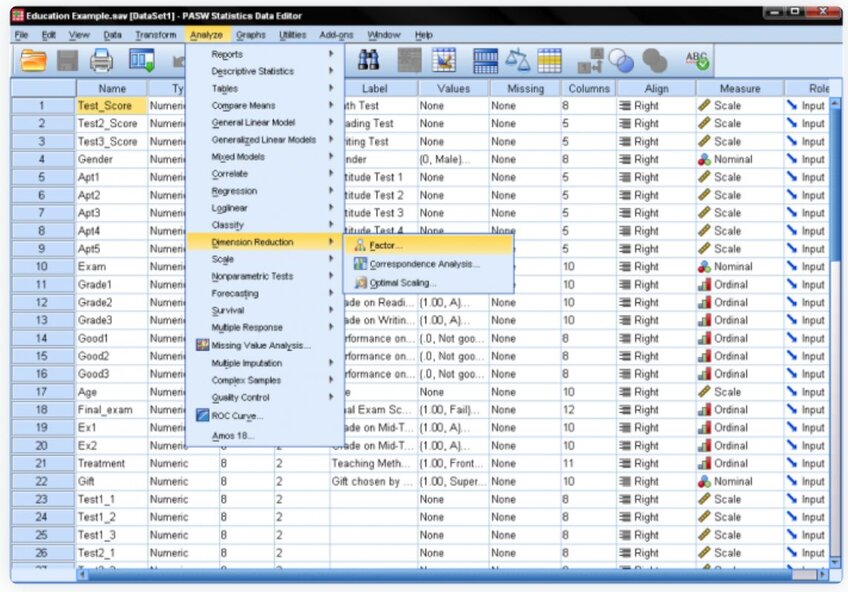
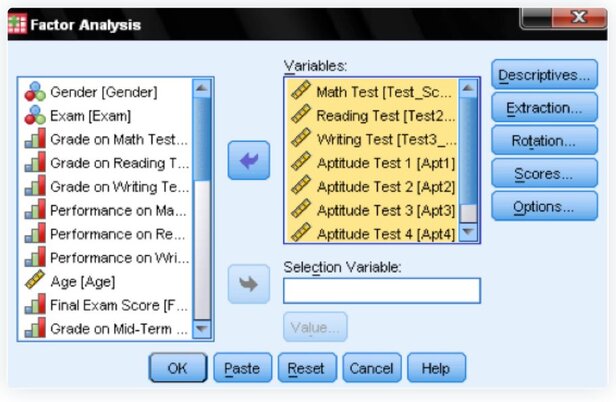
2.) Add Variables: Insert the standardized tests (math, reading, writing) and aptitude tests (1-5) to the list.
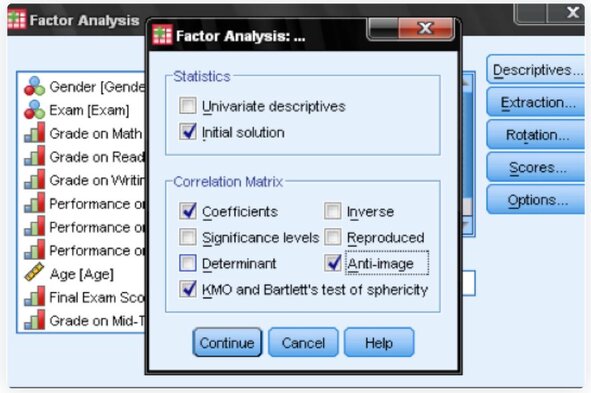
3.) Descriptives: To verify assumptions, include the KMO test of sphericity and the Anti-Image Correlation matrix.
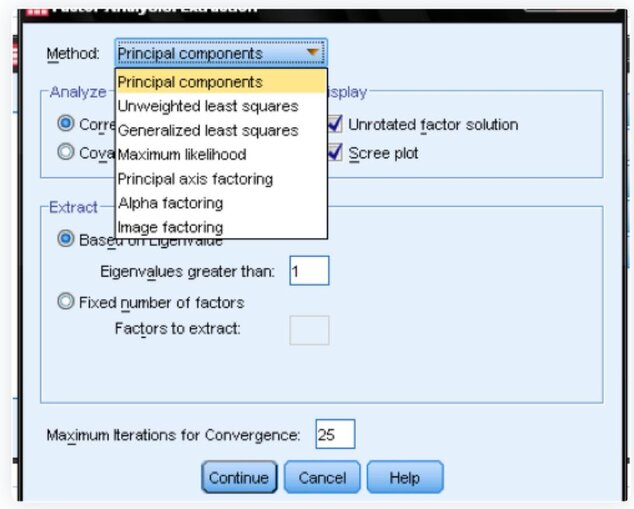
4.) Extraction Method: While SPSS defaults to 'principal components', for identifying latent constructs, 'principal axis factoring' is more apt.
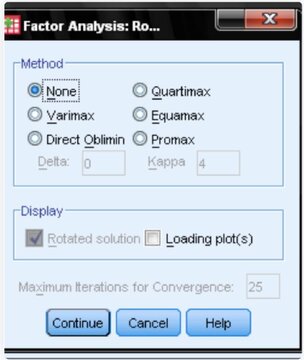
Conclusion
Factor Analysis is an indispensable tool for researchers and analysts aiming to uncover hidden patterns and dimensions in their data. While SPSS offers robust capabilities for factor analysis, it's essential to understand the nuances and steps involved to derive meaningful insights.
While SPSS has been a stalwart in the realm of statistical analysis, the digital age demands more agile and intuitive tools. Enter Julius.ai, a cutting-edge platform designed for modern analytical needs. Whether you're diving deep into factor analysis or exploring other statistical realms, Julius.ai offers a seamless, user-friendly experience. Say goodbye to cumbersome processes and hello to streamlined, efficient data analysis with Julius.ai.
