March 10th, 2025
How Do AI Chatbots Actually Work? Your Helpful, In-Depth Guide
By Connor Martin · 8 min read

It is the age of artificial intelligence (AI), and AI chatbots are everywhere. They’re on phones, computers, online stores, brand websites, tech support networks, streaming services, and even pizza delivery platforms.
Harnessing the power of natural language processing, these AI tools have the added benefit of being a time-saving technology. They are great for routine tasks, responding to customer requests, and providing support and other services.
But have you ever wondered how, exactly, they work, and what kinds of technology they rely on to respond to your inputs? This guide will shed some light on that, exploring how AI chatbots work and examining some of their real-world applications.
Key Takeaways
• AI chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to interpret user inputs, generate responses, and improve over time through data analysis.
• They come in various types, from rule-based to generative models, with applications in customer service, e-commerce, healthcare, banking, and internal business automation.
• While AI chatbots enhance efficiency and engagement, they have limitations, including struggles with complex queries, contextual awareness, and the need for continuous training.
What Is an AI Chatbot?
We’ll begin with the basics and a look at what chatbots actually are.
The concept of chatbots has been around for quite a while. Several decades, in fact, as the first chatbot (albeit a very primitive one compared to today’s models) was made in the 1960s. It was designed to imitate conversation, delivering a set of canned responses to fit the user’s textual input.
Since then, many other chatbot formats have followed. They were often given simple decision-tree rules or menus to follow to give the user a fitting reply to their query or demand. However, the technology and competency have improved over time.
Modern-day AI-powered chatbots, also sometimes called virtual assistants or simply bots, take this concept to a higher level. They use technologies like natural language processing and machine learning to interpret user or customer queries and generate responses on the fly.
They provide more realistic, human-like customer interactions and personalized responses than the bots of the past. They can be used in numerous settings, and are often employed in fields like customer service, tech support, education, and automated booking/reservation systems.
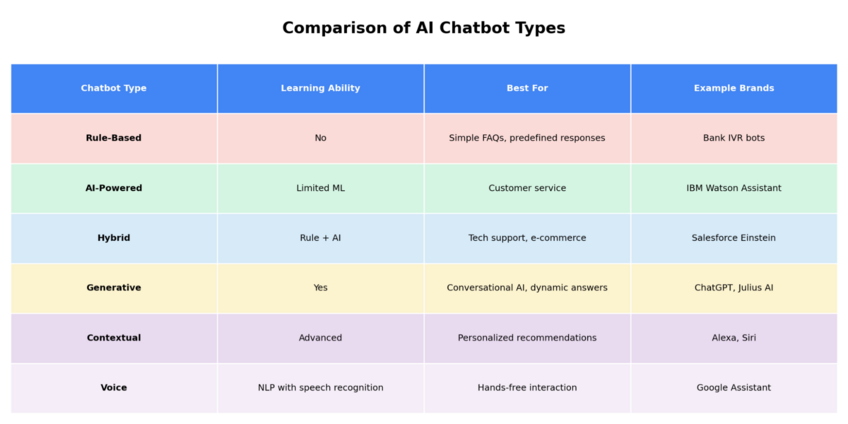
Types of AI Chatbots
AI-powered bots can be classified according to different groups based on their intelligence levels, capacities, and ways of interpreting customer data and generating responses.
• Rule-Based: These are among the most rudimentary types of chatbots. They’re basically programmed with a set of rules they have to follow. Every time they receive input, they follow the decision tree of their ruleset to lead them to the best possible response.
• AI-Powered: Most chatbots nowadays are AI-powered, meaning they have some sort of artificial intelligence “mind” interpreting each input and selecting or generating a reply. This helps them deliver more fitting and helpful responses.
• Hybrid: Hybrid models essentially combine the technologies of the previous two. They have AI to oversee their decisions but also have a strict set of rules to follow when delivering responses, which makes them very practical for repetitive tasks and niche uses, like tech support.
• Generative: Generative chatbots are empowered with generative AI technology to create unique answers for every input. This makes conversations feel both more dynamic and organic, which can aid in user satisfaction and overall utility.
• Machine Learning/Contextual: These are the most advanced types of AI chatbots on the market today, with contextual awareness and learning capabilities. This means they can figure out the context behind a user’s input and learn from each interaction to improve over time.
• Voice: Voice conversational AI chatbots are those capable of interacting with users via voice. They can interpret a user’s voice input and respond with vocal replies of their own, which may aid with customer engagement.
What’s the Technology Behind AI Chatbots?
The tech underpinning today’s leading workplace AI chatbots is highly advanced and made up of several core components:
• Natural Language Processing (NLP): The backbone of all modern AI systems is NLP, which is the tech that allows AI models and bots to understand human language. Utilizing deep learning, NLP empowers chatbots to figure out what a user wants, based on their text/voice input.
• Machine Learning: Machine learning is a broad term referring to the development of machines or digital systems (like bots) that can learn, adapt, and grow over time. They do so through usage and autonomous analysis, without the need for human intervention, code improvements, etc.
• Intent Recognition: This is the ability of a bot to figure out what a user’s intent is, based either solely on their input or their input combined with other contextual clues. The more advanced bots and agents have the ability to understand the context to better understand the user’s needs.
• Entity Extraction: Also called entity chunking, this is a part of NLP technology. It’s what allows chatbots and AI tools to draw the relevant information they need to give to the user from the vast amounts of data available to them.
• Dialog Management: Chatbots also need to be able to manage the back-and-forth flow of a conversation to keep the user engaged and meet their needs. Strong dialog management aids with customer retention and customer satisfaction.
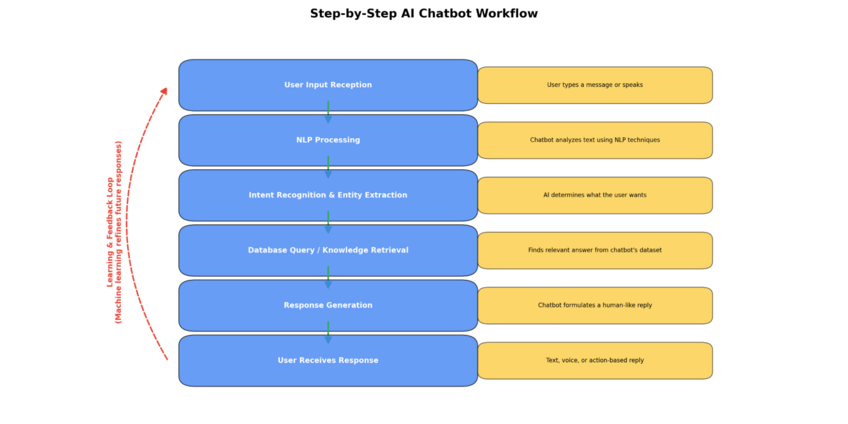
Step-by-Step of How AI Chatbots Work
The exact way chatbots work varies from bot to bot based on their technology and programming. The steps below show a general workflow for a typical generative AI chatbot:
#1 - User Input Reception
The first step is the receipt of the user’s input. Many chatbots work with text, so the user will type out the question they want to ask or the subject they want help with, and send it to the bot. That data will be transmitted to the relevant servers and delivered to the bot in question, ready to be processed, interpreted, and responded to.
#2 - Input Processing (with NLP)
Next, the chatbot gets to work figuring out what the user is asking for. This is where NLP comes heavily into play. The bot will typically break down the user input into text fragments and look for pattern recognition, cross-referencing with existing datasets, and training to get a clear picture of the user’s demand.
• Customer Services: One of the most common uses of chatbots nowadays is in customer service. Many retail brands and other businesses have helpful bots on their sites that will answer common user queries. Some of these bots also provide promotional services, urging users to directly get in touch with the business, for example.
• Tech Support: Many tech firms have invested heavily in AI chatbots and trained them to provide common support services to users. Users who may have issues with their everyday electronic devices, for example, can speak with these bots and solve routine problems on their own or get redirected to helpful guides and tutorials.
• E-Commerce: The e-commerce world is awash with AI bots. Many online stores have them to help customers find the exact products they want to buy, for example. Bots can also assist customers with placing their orders, requesting refunds, making complaints if they’re not satisfied with what they have received, etc.
• Healthcare: In healthcare, bots are increasingly being utilized by clinics, dental practices, and other establishments to provide immediate, non-urgent support to patients in need. Patients can provide information about the situation and get help from the bots with making appointments or treatment recommendations.
• Banking: More and more banks are turning to AI chatbots to help account holders access certain services, get responses to common queries, find the right financial products for their needs, etc. There may also be internal usage of these bots, helping bank employees quickly access customer data without having to manually trawl through databases.
• Hospitality: Businesses in the hospitality industry – hotels, restaurants, etc. – are increasingly employing AI chatbots to help with customer queries, particularly reservations. Customers can now engage with these bots to make bookings for specific dates and times or request special services, without the need to call or speak with a real human worker.
• Internal Business Automation: Many of the uses of AI chatbots are customer-facing. But, as mentioned, there are cases in which businesses may use bots internally to assist workers with their day-to-day operations. Some internally used bots, for example, can take tedious tasks off workers’ hands or save time searching for specific files, getting quick answers to queries, or help using office tools.
• AI Voice Assistants & Answering Services for Small Businesses: Beyond website chatbots, many companies – especially small businesses – are now using AI voice assistants and AI answering services to handle incoming phone calls. These AI voice agents can answer frequently asked questions, route calls to the right department, book appointments, collect customer information, and provide 24/7 phone support. For small businesses in particular, AI-powered answering services offer a cost-effective alternative to hiring full-time reception staff while ensuring that no customer call goes unanswered.
#3 - Retrieval of Relevant Information
Next, once the bot knows what it needs to do, it can get to work sourcing the relevant information to generate a suitable response. This ties into the entity extraction technology, discussed earlier. The bot will consult its databases to seek out the necessary data, all in mere seconds or even fractions of seconds.
#4 - Response Generation and Delivery
With the relevant data gathered the chatbot can then generate a response. Again, NLP ties into this and dialog management, in order for the bot to deliver a response that is relatable, engaging, and efficient. It may generate pleasantries or additional info to supplement the main response, depending on its programming.
#5 - Learning and Adapting from Interactions
The best bots are also capable of learning from each interaction, so they log conversation data to analyze and review later. In some cases, they will remember exactly what users have asked them or what info they provided, to make future interactions with the same people more fluid and personalized.
Key Components of an AI Chatbot Architecture
To better understand how AI chatbots work, it helps to look at the technologies and architecture components that power them, which include:
• Front-End Interface: The front-end of any AI chatbot is the user-facing part. This is what people see when they want to type in a query, get instant support, etc. For a smooth and positive customer experience, front-end interfaces need to be sleek and simple, so that even beginner users have no problems typing in their requests and getting AI aid.
• Back-End Processing: The back-end is the part that users don’t see, the “under the hood” technology that does all the processing and interpretation of users’ inputs. Many bots’ back-end systems feature question-and-answer models, in which the bot interprets a user’s question by breaking it down into fragments, and then seeks the relevant answer from its database.
• AI Model Training/Optimization: AI models have to be trained to build up their intelligence levels, knowledge, and capacities. Some models are manually trained, which involves manually listing typical user queries and mapping the relevant answers. Others have automated training, in which the bot learns on its own through data analysis and various resources.
• Integration with External Systems: Many AI chatbots boast custom integrations, allowing them to work seamlessly with an array of other tools and systems. For example, you can integrate chatbots with your online store, your customer relationship management platform (CRM), or certain social media accounts.
• Traffic/Node Server: This is the part of the chatbot that receives user data, sent from the user’s devices to the chatbot server, and then sends that data onward to the bot itself. It also takes the response data from the bot and then sends that back out to the user on the other end, facilitating communication between the two parties.
Real-World Applications of AI Chatbots
• Customer Services: One of the most common uses of chatbots nowadays is in customer service. Many retail brands and other businesses have helpful bots on their sites that will answer common user queries. Some of these bots also provide promotional services, urging users to directly get in touch with the business, for example.
• Tech Support: Many tech firms have invested heavily in AI chatbots and trained them to provide common support services to users. Users who may have issues with their everyday electronic devices, for example, can speak with these bots and solve routine problems on their own or get redirected to helpful guides and tutorials.
• E-Commerce: The e-commerce world is awash with AI bots. Many online stores have them to help customers find the exact products they want to buy, for example. Bots can also assist customers with placing their orders, requesting refunds, making complaints if they’re not satisfied with what they have received, etc.
• Healthcare: In healthcare, bots are increasingly being utilized by clinics, dental practices, and other establishments to provide immediate, non-urgent support to patients in need. Patients can provide information about the situation and get help from the bots with making appointments or treatment recommendations.
• Banking: More and more banks are turning to AI chatbots to help account holders access certain services, get responses to common queries, find the right financial products for their needs, etc. There may also be internal usage of these bots, helping bank employees quickly access customer data without having to manually trawl through databases.
• Hospitality: Businesses in the hospitality industry – hotels, restaurants, etc. – are increasingly employing AI chatbots to help with customer queries, particularly reservations. Customers can now engage with these bots to make bookings for specific dates and times or request special services, without the need to call or speak with a real human worker.
• Internal Business Automation: Many of the uses of AI chatbots are customer-facing. But, as mentioned, there are cases in which businesses may use bots internally to assist workers with their day-to-day operations. Some internally used bots, for example, can take tedious tasks off workers’ hands or save time searching for specific files, getting quick answers to queries, or help using office tools.
• AI Voice Assistants & Answering Services for Small Businesses: Beyond website chatbots, many companies – especially small businesses – are now using AI voice assistants and AI answering services to handle incoming phone calls. These AI voice agents can answer frequently asked questions, route calls to the right department, book appointments, collect customer information, and provide 24/7 phone support. For small businesses in particular, AI-powered answering services offer a cost-effective alternative to hiring full-time reception staff while ensuring that no customer call goes unanswered.
What Are Some Challenges and Limitations of AI Chatbots?
While AI chatbot technology is an exciting step forward for many industries, it is not without its flaws. It has limitations that prevent it from carrying out all the tasks that workers might like help with, and its reliability levels are not perfect, either.
Some common issues are:
• Difficulty with Complex Queries: Many chatbots can handle common user questions. A tech support bot, for example, will be able to provide quick fixes for basic errors. But if someone presents it with a very specific, complex problem, it may not have the knowledge needed.
• Context: Often, chatbots lack contextual awareness. They are purely data and input-driven, responding solely to the words that a user sends to them. They cannot necessarily understand the external factors of the user’s situation or their emotional state, which can lead to responses that are not entirely suitable and may frustrate the end user even more.
• Privacy/Security Concerns: A lot of sensitive customer data can be fed into chatbots, from customer account numbers to names, addresses, and even payment info. There are risks of that data being accessed, intercepted, or leaked. Bot users have to take necessary steps to safeguard sensitive info and comply with industry regulations.
• Continuous Training: Bots have to be trained and improved regularly to remain relevant and helpful. If they are left to stagnate or have poor autonomous learning capabilities of their own, they may quickly become redundant or even error-prone. Businesses have to therefore invest time and energy into maintaining them.
Future of AI Chatbots
There is a bright future ahead for AI chatbots, as AI technology is still, relatively speaking, in its infancy and has room to grow. As the tech improves and new deep-learning techniques emerge, bots will only get better, smarter, and more efficient.
We can also expect to see more bots with multi-model capabilities (the ability to understand and use data in different formats, like voice, code, and video). Plus, there are many more opportunities waiting to be explored with AI chatbot applications in virtual reality and metaverse settings.
Make the Most of AI (and Sharpen Your Skills) With Julius AI
The best AI bots and agents are capable of far more than merely pasting pre-written responses to user demands. They can carry out in-depth data analysis, statistical visualizations, and tasks that would normally take hours, if not days of work.
Julius AI is one such example. An AI data analyst, Julius AI can work with data in extraordinary ways, with remarkable accuracy and reliability. Test it out today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Where do AI chatbots get their information?
AI chatbots pull their information from a variety of sources, including pre-trained datasets, online knowledge bases, company-specific databases, and real-time inputs from users. More advanced bots use machine learning to continuously refine their responses based on new data and interactions.
How are AI bots programmed?
AI chatbots are programmed using a combination of rule-based logic, machine learning algorithms, and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. Developers train them on large datasets, fine-tune their models, and integrate them with APIs to enhance their functionality.
How do AI bots learn?
AI bots learn through machine learning and deep learning techniques, analyzing vast amounts of data to recognize patterns and improve over time. Some bots also use reinforcement learning, adapting based on feedback from user interactions to refine their accuracy.
What language is used to build a chatbot?
Chatbots are commonly built using programming languages like Python, JavaScript, and Java, with frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and spaCy enhancing their AI capabilities. Many also leverage NLP libraries and cloud-based AI platforms to streamline development.
How do AI chatbots like ChatGPT work?
AI chatbots like ChatGPT use deep learning models, specifically large language models (LLMs), to generate human-like responses. They process user inputs through NLP, analyze context, and generate responses based on their training data, making conversations feel more natural and dynamic.
